
Since we are working on saving you time though, your most efficient results will involve you memorizing the following 10 atoms. This is a must-learn checklist – so if you didn’t watch yet, review this video:Īs you work through Lewis Structures it helps to have a periodic table handy. As you get more comfortable with this topic you’ll be able to pick out bonds on skeletal bond-line drawings.įor now, let’s stick with the basics (or better – Let’s keep it simple), and look at a handful of examples utilizing the checklist shared in the Lewis Structures video below. When you first study formal charge it helps to draw out the Lewis Structure for every molecule in question. Want to see this shortcut brought to life? See my formal charge video below Lone pairs represent 2 electrons sitting on the atom so that Has = 2Įach bond only counts for a single electron since the second electron in the bond is touching the other atom. Has = the number of electrons an atom HAS directly attached, touching the atom in question. Should = the number of valence electrons that a neutral atom SHOULD have. Let’s make sure you understand this shortcut
Formal charge of carbon how to#
This shortcut is guaranteed to save precious seconds on your exam IF AND ONLY IF you understand how to apply it.īut when you understand it you’ll be able to solve formal charge in your head, in under 8 seconds per atom.

Here another option, MY version – one that is easier, faster, and comes out with the same result! Formal Charge Calculation Shortcut Yes the equation works, but it’s far too tedious and annoying! There are just too many steps and calculations. A triple bond of 6 electrons allows each atom to claim three.ĭo you dread running through this every time you finish a reaction?
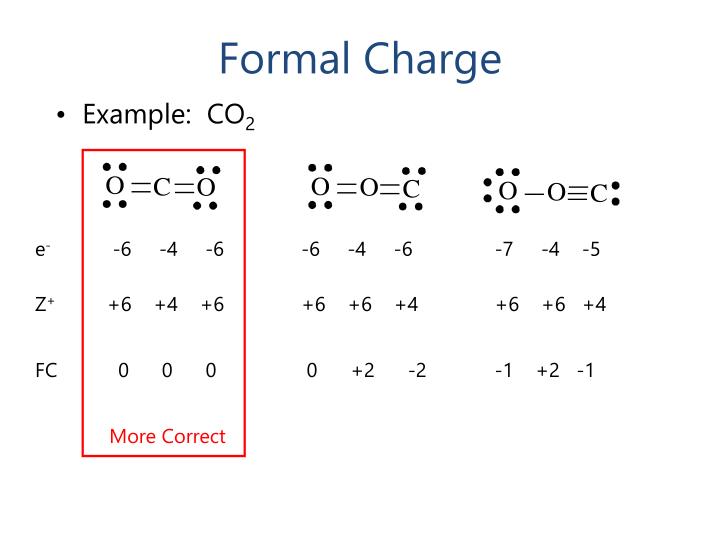
A double bond containing four electrons allows each atom to claim 2.

Formal charge helps you understand reaction patterns by showing you why a specific atom attacks, and why its ‘victim’ accepts the attack. Yet understanding the nature of Formal Charge is a critical component when it comes to mastering organic chemistry reactions and mechanisms. How can you afford that kind of time when working through a multi-step synthesis? Formal Charge is that pesky concept covered early in organic chemistry and somehow never seems to go away.īecause the equation in your textbook is long, confusing, and needlessly annoying.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
